medical condition affecting the nose, possibly rhinophyma, a severe form of rosacea, or another skin-related disorder involving tissue overgrowth
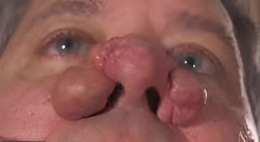
This image appears to show a medical condition affecting the nose, possibly rhinophyma, a severe form of rosacea, or another skin-related disorder involving tissue overgrowth. If you’re looking to prevent such conditions, here are some general tips:
Prevention Tips:
-
Skin Care & Hygiene:
- Wash your face with gentle cleansers.
- Avoid harsh soaps or scrubs that irritate the skin.
-
Manage Rosacea (If At Risk):
- Avoid triggers like spicy foods, alcohol, hot drinks, and extreme temperatures.
- Use sunscreen daily to protect sensitive skin.
-
Healthy Lifestyle:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
- Stay hydrated and avoid excessive alcohol or smoking.
-
Medical Check-ups:
- If you notice persistent skin changes or growths, see a dermatologist early.
- Conditions like rhinophyma may be treated with medications, laser therapy, or surgery.
1. Rhinophyma (Severe Rosacea)
Causes:
- Chronic, untreated rosacea
- Overgrowth of sebaceous (oil) glands in the nose
- More common in men over 50
Symptoms:
- Thickened, lumpy skin on the nose
- Enlarged pores
- Red or purple discoloration
- Visible blood vessels
Prevention & Treatment:
- Early treatment of rosacea with medications (topical or oral antibiotics)
- Laser therapy or surgery for advanced cases
- Avoid triggers like alcohol, spicy foods, and sun exposure
2. Skin Conditions (Cysts, Fibromas, or Tumors)
Causes:
- Genetic predisposition
- Skin infections or chronic inflammation
- Benign or malignant growths
Symptoms:
- Slow-growing lumps or nodules
- No pain in early stages, but may become tender
- Sometimes associated with bleeding or ulceration
Treatment:
- Dermatological evaluation
- Biopsy if needed
- Surgical removal if necessary
3. Severe Acne or Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Causes:
- Excessive oil production
- Hormonal changes
- Chronic inflammation of skin follicles
Symptoms:
- Persistent white or yellowish bumps
- Enlarged oil glands
- Waxy or bumpy skin texture
Treatment:
- Prescription creams (retinoids, benzoyl peroxide)
- Laser therapy
- Oral medications (isotretinoin for severe cases)
4. Basal Cell Carcinoma (Skin Cancer)
Causes:
- Long-term sun exposure
- Fair skin, older age, or genetic factors
Symptoms:
- Pink or flesh-colored bumps
- Slow-growing lesions that may ulcerate or bleed
- May resemble a sore that doesn’t heal
Treatment:
- Surgical removal or Mohs surgery
- Radiation therapy for advanced cases
Next Steps:
If you or someone you know has symptoms like these, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. Early treatment can prevent worsening and improve outcomes.


